| Not logged in : Login |
About: Nike Business Model: Demand Generation As Weapon For Business Growth Goto Sponge NotDistinct Permalink

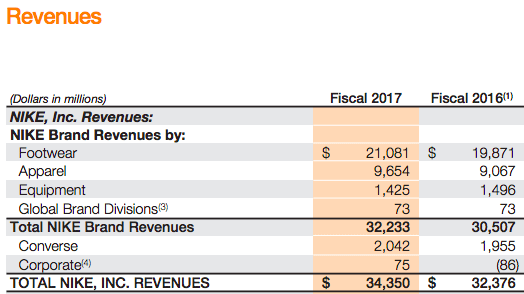
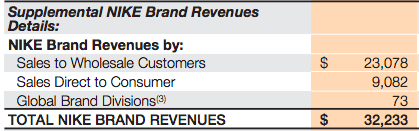
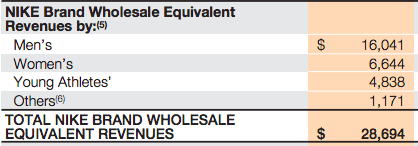
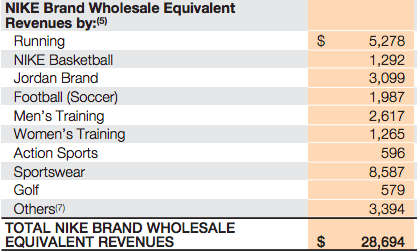
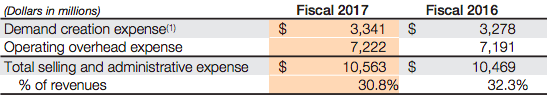
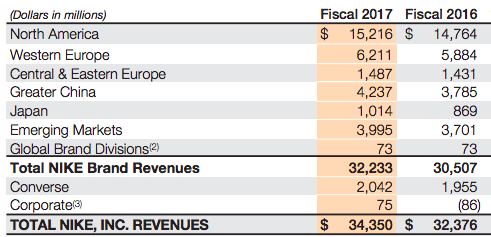
Nike makes money by primarily selling footwear via wholesale customers that distribute the Nike brands across the globe. As of 2017, over 60% of revenues came from footwear and over 28% in apparel. The remaining comprised equipment and the Converse Brand. One of the critical ingredients of Nike business model success is its ability to create demand for its products. In fact, as of 2017 Nike spent over $3.3 billion in demand creation campaigns. What products does Nike sell? Nike has nine key categories: Running, NIKE Basketball, The Jordan Brand, Football (Soccer), Men’s Training, Women’s Training, Action Sports, Sportswear (our sports-inspired lifestyle products) and Golf. Men’s Training includes baseball and American football product offerings. Nike also markets products designed for kids, as well as for other athletic and recreational uses such as cricket, lacrosse, tennis, volleyball, wrestling, walking and outdoor activities Nike distribution and manufacturing NIKE has six significant distribution centers located in Memphis, Tennessee, two of which are owned and four of which are leased. Nike is supplied by approximately 127 footwear factories located in 15 countries. The largest single footwear factory accounted for about 8% of total 2017 NIKE Brand footwear production. All of Nike footwear is manufactured outside of the United States by independent contract manufacturers who often operate multiple factories. In 2017 Vietnam, China and Indonesia manufactured approximately 46%, 27% and 21% of total NIKE Brand footwear, respectively. Nike revenues breakdown With $21 billion revenues in 2017, footwear represents the 61.5% of the total income. Followed by Apparel, with $9.6 billion and the Converse segment with over $2 billion in revenues. Global Brand Divisions revenues are primarily attributable to NIKE Brand licensing businesses that are not part of a geographic operating segment. NIKE Brand wholesale equivalent revenues consist of: Sales to external wholesale customers and internal sales from our wholesale operations to our Direct to Consumer operations, which are charged at prices that are comparable to prices charged to external wholesale customers. Others include all unisex products, equipment, and other products not allocated to Men’s, Women’s and Young Athletes’. Men's sales represent most of Nike total revenues. Running and sportswear are the categories that generate the most revenues for the company. North America represents the most significant market for Nike. Greater China follows. Nike spending on demand creation One key ingredient of Nike success seems to be the demand creation. Demand creation expense consists of advertising and promotion costs, including costs of endorsement contracts, television, digital and print advertising, brand events, and retail brand presentation. Demand creation expense increased 2% for fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016, driven by higher sports marketing costs, as well as higher marketing and advertising costs, primarily to support key sporting events including the Rio Olympics and European Football Championship. How does Nike record demand creation? The Company records demand creation expense for these amounts when the endorser achieves the specific goal. Certain contracts provide for variable payments based upon endorsers maintaining a level of performance in their sport over an extended period of time (e.g., maintaining a specified ranking in a sport for a year). When the Company determines payments are probable, the amounts are reported in Demand creation expense ratably over the contract period based on the Company’s best estimate of the endorser’s performance. Yet the extent that actual payments to the endorser differ from the Company’s estimate due to changes in the endorser’s performance, increased or decreased demand creation expense may be recorded in a future period. Other contracts provide for royalty payments to endorsers based upon a predetermined percent of sales of particular products. Through cooperative advertising programs, the Company reimburses customers for certain costs of advertising the Company’s products. Gotta give them props -- they know where their bread is buttered. Can't just serve searchers for "sneakers," and "running shoes." Gotta create demand to grow+thrive. — Rand Fishkin (@randfish) September 22, 2018 Handpicked related articles: What Is a Business Model? 30 Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained How Does Twitter Make Money? Twitter Business Model In A Nutshell How Does DuckDuckGo Make Money? DuckDuckGo Business Model Explained How Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a Nutshell How Does Netflix Make Money? Netflix Business Model Explained How Does PayPal Make Money? The PayPal Mafia Business Model Explained How Does WhatsApp Make Money? WhatsApp Business Model Explained How Does Google Make Money? It’s Not Just Advertising! How Does Facebook Make Money? Facebook Hidden Revenue Business Model Explained Marketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your Business The Google of China: Baidu Business Model In A Nutshell
| Attributes | Values |
|---|---|
| type | |
| label |
|
| label |
|
| sameAs | |
| Description |
|
| depiction | |
| name |
|
| url | |
| legalName |
|
| http://www.w3.org/2007/ont/link#uri |
Alternative Linked Data Documents: PivotViewer | iSPARQL | ODE Content Formats:
![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png) RDF
RDF
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png) ODATA
ODATA
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[odata+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png) Microdata
Microdata
![[microdata+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png) About
About


![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)
OpenLink Virtuoso version 08.03.3331 as of May 21 2024, on Linux (x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25), Single-Server Edition (7 GB total memory, 5 GB memory in use)
Data on this page belongs to its respective rights holders.
Virtuoso Faceted Browser Copyright © 2009-2024 OpenLink Software